The word ‘titanium’ sounds familiar.
But what are its properties and how is it used in familiar objects? This is one of the elements that is difficult to answer for such questions.
This article will explain titanium.
This section also introduces the properties of titanium, how it is used in society, the etymology of the word and who discovered it.
This element has interesting properties, so let’s learn about them together.
Contents
Properties and characteristics of Titanium

Titanium is a light and hard element.
It is tough enough to withstand high temperatures and is rust resistant.
On the other hand, there are drawbacks such as high prices and difficulties in processing.
It also has the property of forming a thin oxide film on the surface, which prevents rust from progressing to the interior and, thanks to this film, is less likely to cause metal allergies.
In nature, it is abundant in rocks and exists in the form of ‘ rutile ‘ and ‘ sphene ‘.
Incidentally, the ‘moon rock’ brought back by Apollo 11 contained a few per cent titanium.
Let’s look at how they are used in society, one by one.
How Titanium is used in society.
Titanium is used as an ingredient in ‘shape memory alloys’, ‘dental implants’ and ‘white pigments’.
Let’s look at each of them.
Titanium is useful “shape memory alloy”

Alloys combining titanium and nickel are used as shape memory alloys, as they have the property of returning to their original shape after deformation.
Recently, shape memory alloys have been used for eyeglass frames.
Incidentally, old mobile phones had extendable antennas and the antenna material was also a shape memory alloy.
Titanium is useful “dental implant”
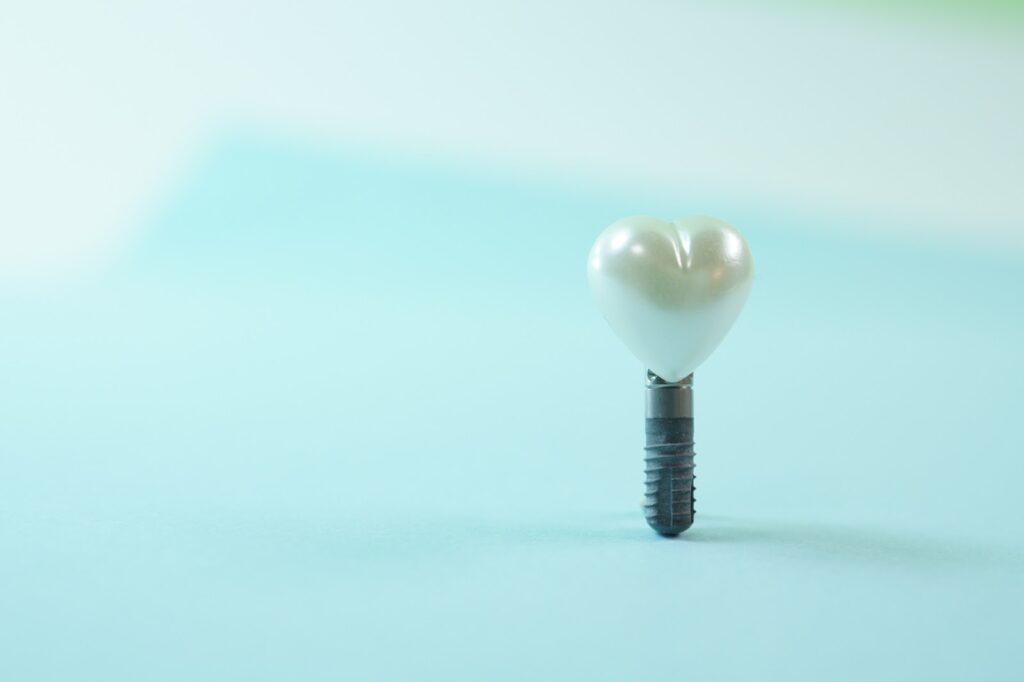
Implant treatment, which has attracted a lot of attention in recent years, is one of the treatments for missing teeth, and the body of the implant used in the treatment is made of titanium.
The implant is placed in the jaw bone, and titanium actually bonds easily to the bone and integrates with it.
Titanium is useful “White pigments”

White pigments (water-insoluble paints) are mainly composed of titanium dioxide.
Commonly known as ‘titanium white amber’.
It is not easily affected by light, heat or chemicals, and is non-toxic, making it easy to use for many things.
History of Titanium

Chemical symbol; Ti
The word titanium is derived from the Greek mythological giant ‘Titan’.
The Titans, defeated in battle against the Olympian gods, were imprisoned beneath the earth. From this myth, the element trapped within ore was named “titanium.”
As for its discovery, Gregor discovered it and the German scientist Klapprodt announced that it was a unique oxide, which was then named ‘titanium’.
Summary
In this article, we have explained ‘titanium’.
The key points of this article are as follows.
Titanium is light, hard and rust-resistant.
Used in ‘shape memory alloys’, ‘dental implants’ and ‘white pigments’.
The other elements studied in high school are summarized in the following articles.
Please see also the following pages for a further understanding!






