
It is said that the history of ship has begun with the birth of mankind.
At first, they used trees floating in the water to across the river, or bundled tree branches to carry loads…
As human civilization developed, ships have been also developed rapidly and came in many shapes and forms.
Moreover, the boats were getting bigger and bigger.
As they got bigger, the number of people maneuvering the boat increases.
As the number of people increased, such as the person at the helm, the person who paddles the oars and the person who controls the sails, a common boat’s name naturally developed.
In this article, we would like to share information about the names of ship’s parts.
Explaining the names of the various parts of the ship in diagrams
The following diagram illustrates the traditional names.
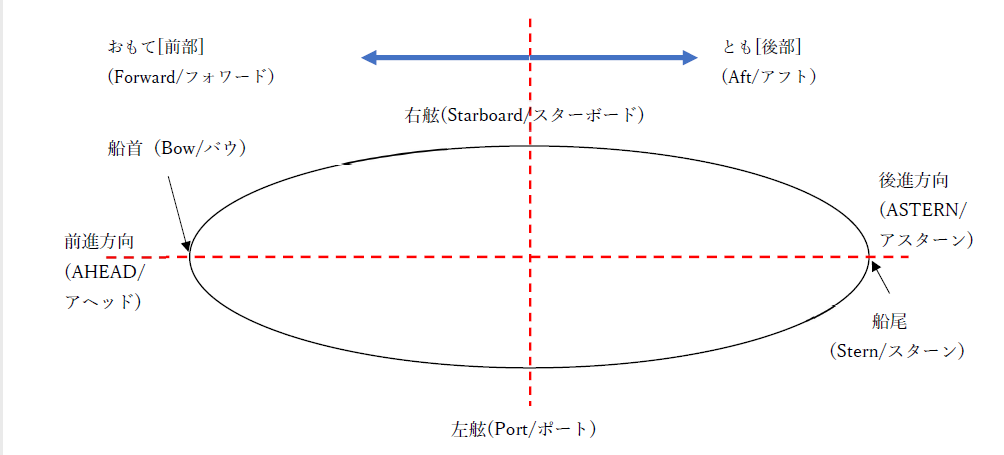
Here’s the origin of the name!
Starboard
During the time of the Vikings, the rudder on Viking ships was attached to the starboard side of the stern, which is said to have changed from Steer Board, meaning ‘helmsman’s side’.
Port
In the same period with the Vikings, the port side of the ship was moored to shore to avoid breaking the rudder as it was on the starboard side.
The ‘shore side’ is said to have become Port.
Bow
As the name suggests, the bow is shaped like a bow.
Next, we will introduce the names of ship built in relatively modern times.
After the Industrial Revolution, when technology advanced dramatically and ships made of steel could be powered by coal or petroleum fuel, the structure has also changed significantly.
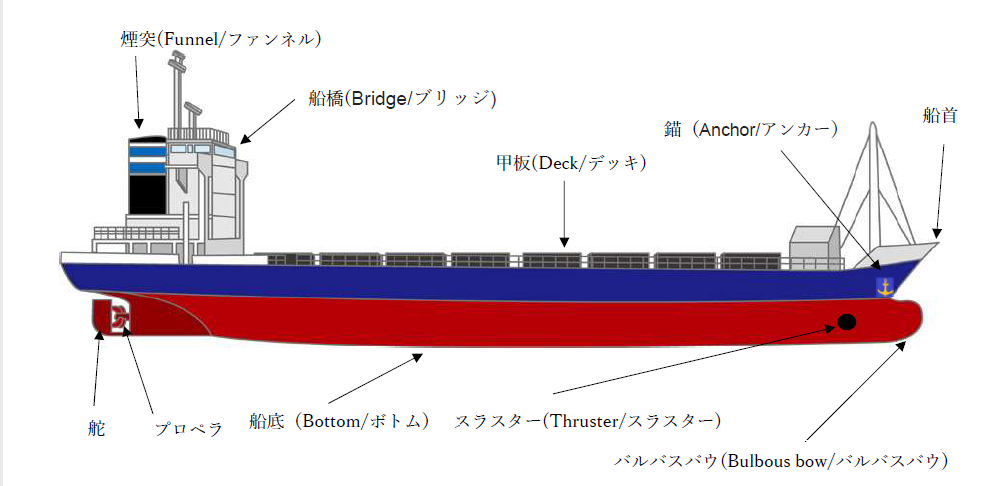
Bridge
In the days when outer-wheeled vessels were the norm, it was necessary to see the whole area from a height in order to check safety left, right, front and rear.
A long, narrow passageway was built like a bridge from starboard to port at the high point of the ship to ensure safety, and from there the whole ship was directed in the direction of travel.
Today, the boat can be maneuvered on the ship’s bridge.
Thruster
There is an electric motor-powered propeller in the hole. Landing a ship alone.
An engine and propeller cannot move a ship straight across.
To move the vessel straight across, a vessel (tugboat) or this thruster is used to push the vessel to shore.
Anchor
Anchors are sunk to the seabed to keep the vessel in a certain area above water.
It is not understood when they exist.
In Japan, it has been excavated from sites dating from about 1300 to 2300 years ago.
In the early middle of the 10th century, stones in the sea were referred to as ‘ikuri’ and called the origin of the word, but the relevance has not been clarified.
Bulbous bow
It was invented in the first half of the 20th century to improve fuel efficiency and speed.
The water pushed away by the hull creates waves that reduce the speed and fuel consumption of the ship (wave-making resistance).
This wave-making resistance is counteracted by the waves created by the bulbous bow.
In Japan, the Battleship Yamato was the world’s first to adopt the system, which at that time was said to have saved approximately 8% of energy.
How was it? Of course, the names introduced here are not all of them. Look them up if you’re interested!
Further reading.
What fuel is generally used for ships?
AGUS fabricates a wide range of marine equipment as well.





